Buildings are becoming micro-energy hubs, but the building sector is lagging behind in understanding the implications.
(A version of this article was published on The Fifth Estate on 10 July 2017.)
This problem is to be tackled from one direction by the development of a voluntary “smart readiness indicator” (SRI) for buildings. The SRI would measure buildings’ capacity to use ICT and electronic systems to optimise operation and interact with the grid.
But, just as there’s no consistent data, there is also no universally accepted definition of what makes a smart building, and there are few initiatives directly linked to indicators.
So work is now underway to try to define what an SRI for buildings looks like.
Why do it?
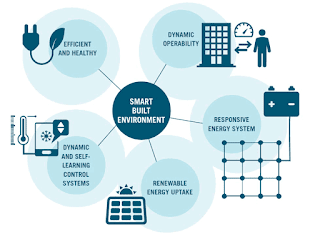 |
| A smart building environment connects with many processes. Source: BPIE |
An SRI would also align building energy performance – and the current drive to create a Single European Energy Market – with another pan-European idea: the Digital Single Market.
The rationale is that digitalisation of the energy system is rapidly changing the energy landscape, allowing easier integration of renewables, smart grids and the establishment of “smart-ready” buildings.
 |
| The benefits of 'smart buildings' Source: BPIE |
As with most things in European legislation, the development of an SRI is complex. It’s bound up with the European Commission’s current process to revise a directive to improve the energy performance of buildings. By 2050, the aim is to decarbonise the building stock as part of developing a secure, competitive and decarbonised Europe-wide energy system.
This revision of the Energy Performance of Buildings Directive (EPBD) was originally meant to incorporate targeted incentives to promote smart-ready systems and digital solutions in the built environment, but has since become less ambitious.
The aim is to promote energy efficiency in buildings and to support cost-effective building renovation with a view to the long term goal of decarbonising the highly inefficient existing European building stock. It’s part of a wider review of the energy efficiency legislation, combining:
- reassessment of the EU’s energy efficiency target for 2030 – which was just set at a lamentably low rate of 27 per cent
- a review of the core articles of the Energy Efficiency Directive and the Energy Performance of Buildings Directive
- reinforcing the enabling financing environment including the European Structural and Investment Funds (ESIF) and the European Fund for Strategic Investments (EFSI)
What is an SRI?
According to the European Economic and Social Committee, a smartness indicator will measure a building’s capacity to use ICT and electronic systems to optimise operation and its interaction with the grid by developing a transparent, meaningful indicator that would add value to the EPC without imposing undue data collection or analytical burdens.Such an indicator would show how capable a building is of letting its occupants assess energy efficiency, control and facilitate their own renewable energy production and consumption, and thus cut energy bills.
A preliminary report for the European Commission’s Energy Directorate by consultants Ecofys with colleagues in a specially created consortium, said these indicators would help with the energy management and maintenance of a building, including automated fault detection; assist in automating the reporting of the energy performance of buildings; assist with data analytics, self-learning control systems and predictive control to optimise building operations; and enable buildings to become active operators in a demand response setting.
 |
| The renewable energy context for 'smart buildings'. Source: BPIE. |
Ecofys with its colleagues is developing the formal definitions for the indicators as Task 1 of a series of five stages up to the proposal of the standard in April next year.
It has listed the ten services that the indicator could cover as: heating, domestic hot water, cooling, mechanical ventilation, lighting, dynamic building envelope, energy generation, demand side management, electric vehicle charging, and monitoring and control.
The SRI must be open and transparent, in order to promote interoperability, or it will not be fit for purpose. This means that companies involved cannot monopolise or impose their own proprietary standards.
 |
| Interoperability means that devices and services are able to talk to each other in the same language. Image: Ecofys |
It also implies a readiness to facilitate the maintenance and efficient operation of the building in a more automated and controlled manner, for example by indicating when systems need maintenance or repair, or using CO2 sensors to decide when to increase ventilation.
According to Paul Waide and Kjell Bettgenhäuser of Ecofys, speaking at the first conference on this topic in June, “The SRI should balance the need to reliably capture the smart readiness services and functions with the practicality and potential costs of independent assessment. It needs to be practical and provide the most benefit for the effort and cost of assessment.”
Above all, they said, “It needs to convey information which is salient (meaningful) to end-users, be easy to understand and motivate them to save energy.” It will also have to apply to all types of buildings, new and old.
 |
| An example of how the indicator could work. |
This development process is expected to be complete by April 2018. Anyone interested in following or participating in the development of the indicator can sign up.
David Thorpe is the author of a number of books on energy efficiency, building refurbishment and renewable energy. See his website here.


 All over the world, individuals, groups, towns and cities are struggling with the knowledge that in total, humanity's activities breach the ability of the planet to support them. There is a wide variety of initiatives and programs which are being developed to try to address this and in my
All over the world, individuals, groups, towns and cities are struggling with the knowledge that in total, humanity's activities breach the ability of the planet to support them. There is a wide variety of initiatives and programs which are being developed to try to address this and in my